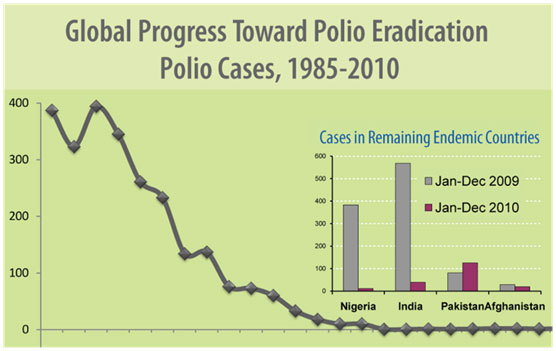
In this section i2P looks at the effect of human population, and population growth on our ability to provide healthcare to the people of the world. Please review the material and answer the two questions in this section.
To illustrate the link between health, population and population growth.
Doctor Availability
In 2008 the United States had 660,000 doctors meaning 1 doctor for every 467 people (provider:patient ratios of 1:467). In comparison, India has 1 doctor for every 1,700 people, much lower than the global average of 1.5 doctors to every 1,000 patients. The rate of population growth combined with relatively low medical school intake indicates that India may have a physician deficit of 954,000 by 2031. Not only is India at risk for a shortage of doctors, but some regions of India are so remote that they do not have access to physicians, instead relying on community health workers (CHW). CHWs include village health workers, community health aides and lay health advisors.
School Question 1
What is the ratio of doctors to population in your community?
Calculate the number of doctors per population and submit below. This number is obtained by the number of doctors in your community by the number of population in your community. This will be compared to the doctor/population ratio in other participating communities, in India and around the world.
Example calculation:
There is an estimated 537929 doctors in India. India's total population is estimated to be 1,050,000,000. In India, the average number of doctors per person is = (537,929) / (1,050,000,000) = 0.00005. This is a small ratio of doctors per person, and to make comparison easier to understand, it is often reported as the number of doctors per 1000 people. Therefore, if there are 0.00005 doctors per person in the country, then the number of doctors per 1000 people = 0.0005 X 1000 = 0.5. Submit the number of doctors per 1000 people for your community.
Birth Rate
Birth rate is the number of children born per 1,000 people per year. Conversely, the death rate is the number of deaths per 1,000 people per year. As you can expect, if birth rate is higher than death rate, the population will rise, and this is what humans have been experiencing to increasing amounts in recent times. Many of your parents will have seen the world population more than double over their lifetimes, from 3 billion people in the early 1960s, to what will be 7 billion people by the end of 2011. At the dawn of civilization, about 10,000 B.C., when we were first starting to cultivate crops, domesticate animals, and settle in towns, the world population was only 1 million people. Even with an increase in population due to food surplus from farms, world population was still only 200 million by A.D. 1. It took until 1804 to reach 1 billion people. The concept of Carrying Capacity (the amount of people that we can sustain on earth). With world population scheduled to keep growing and reach 9 billion by 2050, we will be hard-pressed to find enough land to grow food for an extra 2 billion people. The ability to provide healthcare becomes challenging with population growth, as health resources become less plentiful.
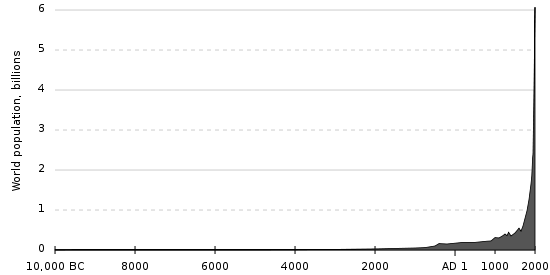
World human population (est.) 10,000 BC–Present time (source: EI T)
School Question 2
How many births are there each year at the hospital in your community?
Submit your response below. This will be compared to birthrates in participating communities, in India and around the world.
Example calculation:
There is an estimated 25,780,000 births per year in India. India's total population is estimated to be 1,050,000,000. To compare birth rates in a country or community, please submit a value for the number of births per 1000 people in your community. For example, using the data for India, the number of births per year per 1000 people = (25,780,000) / (1,050,000,000) X 1000 = 25.












 Source:
Source: 
 Source:
Source: